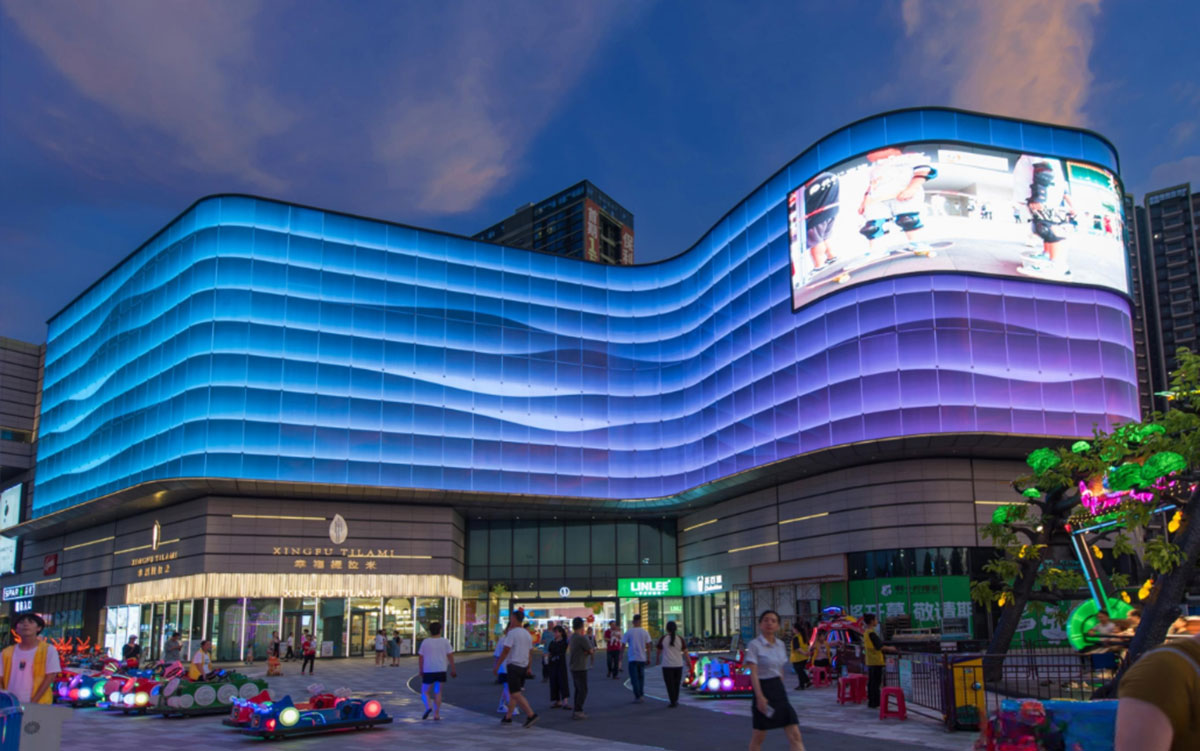
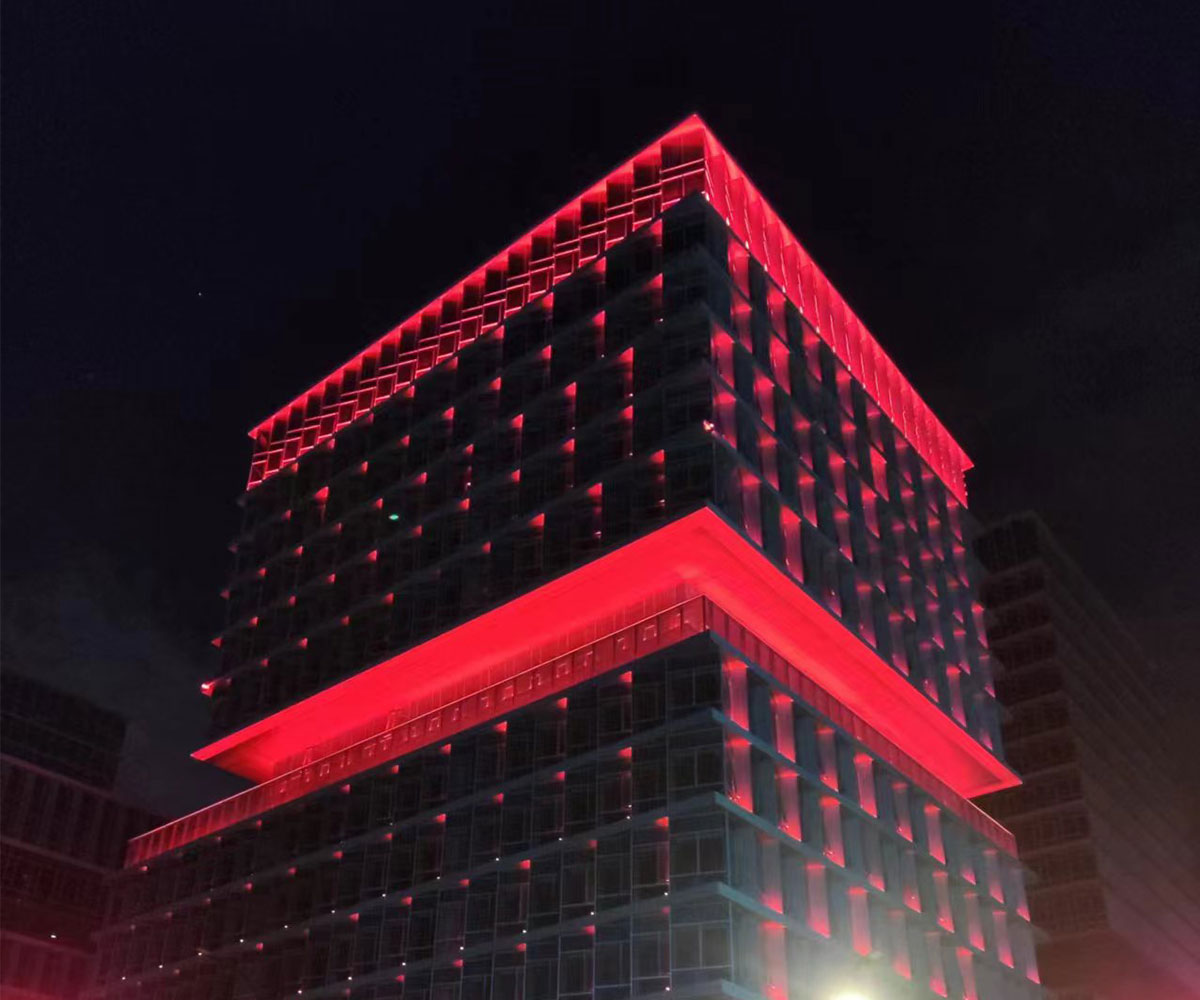
The Guide to Understanding Beam Angle in Lighting
The beam angle is a critical light component that dictates light spread and direction. It is a vital element that determines functionality and ambiance in diverse applications. In any case, it suits light optimization for commercial spaces and residential uses.

1. What is Beam Angle?
The beam angle is the spread of light from a source. You can measure it in degrees since it defines the light cone width, which emits illumination from the source. In other words, it determines how narrowly or broadly the light disperses. This feature is critical in lighting since it affects the illumination intensity and coverage.
To measure the beam angle, you must determine the angle at which the light intensity from the source reduces over a certain percentage of light. In general, the standard measurement uses a 50% light intensity drop.
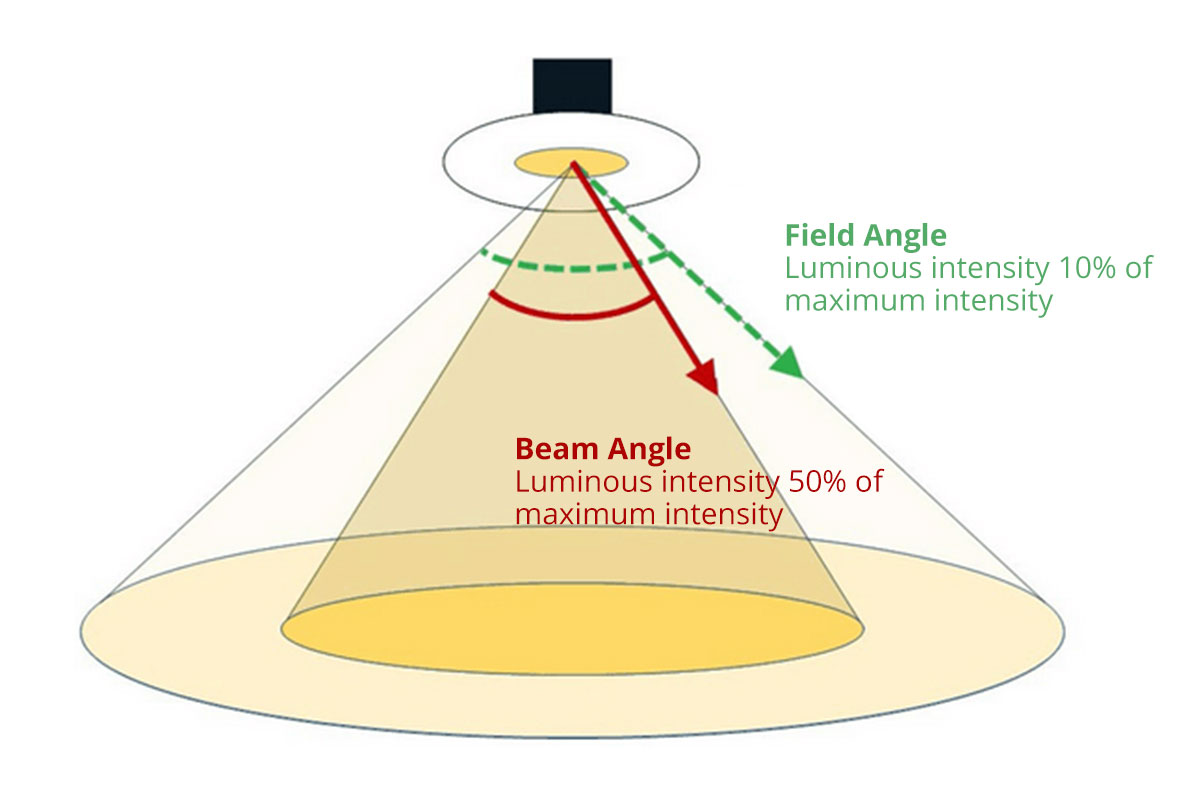
2. Types of Beam Angle
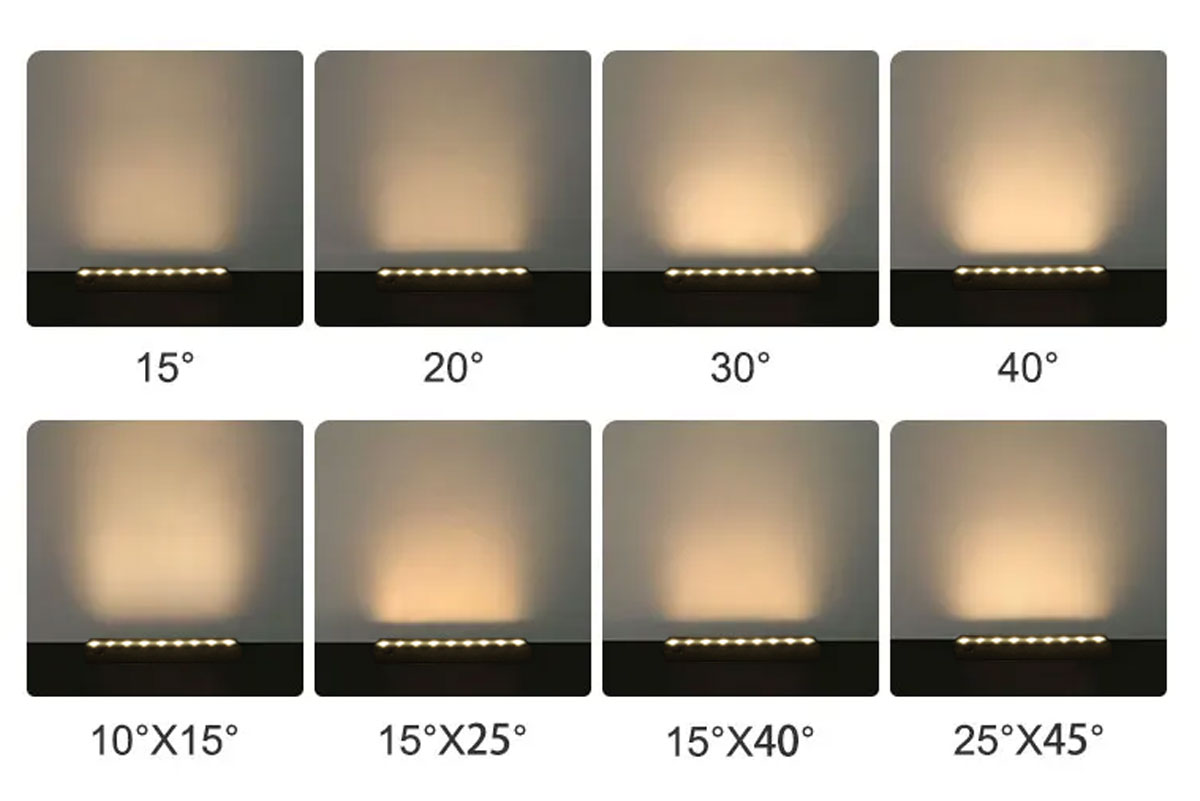
Beam angle can suit diverse applications since it is a critical element in manifesting diverse forms in lighting design. To attain optimized and personalized lighting effects, you must understand various beam angle types. Typical types include wide beam angle, narrow beam angle, and medium beam angle.
2.1) Wide Beam Angle
A wide beam angle is a configuration where light travels over a large area that exceeds 60 degrees. This light spread attains uniform illumination across a larger area to suit ambient settings. Wide beam angles suit outdoor areas, open offices, hallways, and corridors. Overall, they offer consistent brightness for efficient lighting in wide spaces.
2.2) Narrow Beam Angle
A narrow beam angle is a configuration that emits light in a concentrated manner, ranging from 10 to 20 degrees. Thus, it attains focused illumination, creating intense lighting over a small space. This beam angle suits architectural settings.
Narrow beam angles suit uses where attention to detail and precision are critical. Typical uses include artwork, retail displays, and galleries.
2.3) Medium Beam Angle
A medium beam angle is a configuration where illumination spans 30 to 60 degrees to attain balanced lighting. Moreover, it combines broader coverage and focused illumination to suit diverse settings.
Medium beam angles suit commercial and residential settings. Overall, they offer sufficient brightness for larger areas without excessive bright spots and sharp shadows.
2.4) Adjustable Beam Angle
Adjustable beam angle fixtures can spread and direct light according to diverse preferences and needs. You can modify the beam angle using swiveling heads, movable reflectors, and adjustable lenses. These fixtures provide lighting design flexibility and suit diverse settings.
3. Common Applications of Beam Angle
Beam angles serve different purposes in lighting design to suit diverse preferences, requirements, and settings. They are critical in shaping visuals by providing ambient illumination at 20 focal points. However, you must understand typical applications and requirements to attain better results.
3.1) Residential Lighting
The beam angle determines the visual comfort and ambiance for light functionality in residential uses. It is a critical feature in residential lighting design since it allows you to illuminate spaces and implement architectural designs. However, it would help to pick the right fixtures based on the room size, lighting requirements, and design flexibility.
3.2) Commercial Lighting
The beam light is vital for designing a welcoming atmosphere and enhancing visibility for clients in commercial settings. Beam angles minimize glare and attain uniform coverage to display merchandise. Meanwhile, wide beams provide adequate lighting for open-plan offices, while narrow beams suit architectural applications. Maximizing the visual impact and optimizing energy is critical in deciding on the right beam angles.
3.3) Outdoor Lighting
Outdoor lighting is vital for enhancing security and safety. However, the right beam angle is essential for adequately illuminating exterior spaces. This choice can be a strategic approach to promoting landscape features and lighting pathways. Meanwhile, the right beam angle can provide adequate lighting for parking lots and parks.
3.4) Stage Lighting
The beam angle is a critical element for stage lighting since it enhances performance, creates ambiance, and evokes emotion. It promotes performance expression, guides the audience, and shapes the visual narrative.
3.5) Automotive Lighting
Beam angles add a distinctive layer to auto exteriors while optimizing drivers' vision. Manufacturers must engineer the beam angles to meet regulatory requirements. Narrow beams suit headlights since they enable the driver to see far ahead despite oncoming traffic. Wider angles suit fog lights, casting broad light that can penetrate mist.
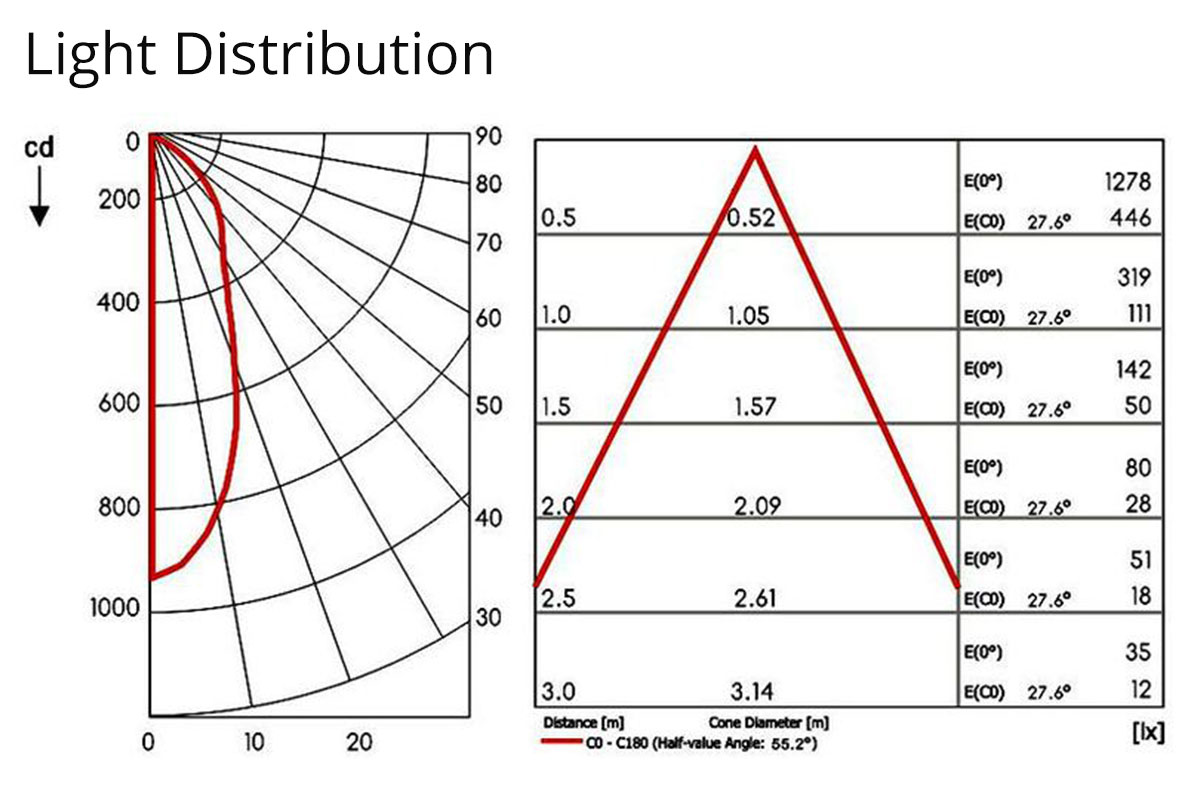
4. Factors Influencing Beam Angle Selection
The beam angle selection focuses on factors contributing to the lighting design outcome. They include the desired lighting effect, space and illumination layouts. These factors determine how the designers can tailor the lighting ambiance to suit diverse uses.
4.1) Purpose of Lighting
The purpose of lighting may vary across diverse applications and settings. The application might aim to create ambiance, promote safety, or enhance visibility in diverse settings such as outdoor, commercial, and residential. In addition, lighting may aim to guide attention, highlight architectural features, or influence mood.
4.2) Space Size & Layout
The space layout and size determine the beam angle and light uniformity. Thus, narrower beam angles suit smaller spaces like corridors and interior rooms to prevent excessive glare and provide focused lighting. On the other hand, larger spaces like offices and halls require wide beam angles to attain uniform brightness.
4.3) Lighting Effect
You must adjust the beam angles for optimal lighting effects, perceptions, and atmosphere. Wider beam angles suit applications that require openness, warmth, and softer illumination. On the other hand, narrow beam angles provide brightened focal points and create dramatic contrast to enhance scene depth.
4.4) Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency is critical in lighting design. The beam angle you choose must match your requirements since it allows you to minimize energy consumption. Simply put, it ensures maximum efficiency, reduces wasted light, and provides precise lighting. Advanced lighting techs such as smart controls and LED lights can be prudent.

5. Conclusion
Beam angle selection is a critical lighting design requirement since it shapes how you interact and perceive environments. It suits outdoor landscapes, commercial settings, and residential spaces to provide strategic functionality, ambiance, and visibility. However, factors like energy efficiency, desired lighting effects, space layout, and lighting purpose are critical for excellent results.
6. Strategize Your Beam Angle Lighting Design with LNJAMI!
Transform your beam angle lighting design with LNJAMI's exceptional lighting solutions. The company offers diverse fixtures for commercial and residential settings. We have experience in precise and creative lighting to meet cutting-edge customer needs. Are you ready to strategize your beam angles today? Visit our website now!








